Why choose Hybrid
Backup Power During Grid Unavailability: Hybrid systems provide backup electricity during grid outages, ensuring continuous power supply even when the main grid is down.
24/7 Power Availability: With hybrid systems, you can have uninterrupted power supply around the clock. They utilize stored energy from batteries and can seamlessly switch between solar, battery, and grid power as needed.
Reduction in Monthly Electricity Bills: By optimizing energy usage and incorporating net metering, hybrid systems help reduce monthly electricity bills. Excess energy generated can be exported to the grid, offsetting consumption costs.
Income from Excess Energy Export: Hybrid systems allow you to earn money by exporting surplus energy back to the grid. This feature leverages excess solar generation and contributes to overall cost savings.
How does it work?
In a hybrid system, the electricity generated by the PV panels is utilized for charging the batteries and is converted from DC to AC at the inverter level to power household loads. When the grid is available, the inverter can also draw power from the grid to charge the batteries during periods of low solar generation, such as rainy or cloudy weather. These systems operate on a net metering basis, similar to on-grid systems. During peak solar generation, excess electricity not needed for charging batteries or powering the home is exported to the grid. This exported energy is credited and balanced against energy imported from the grid. At the end of the billing cycle, the consumer pays only for the net difference between exported and imported energy.
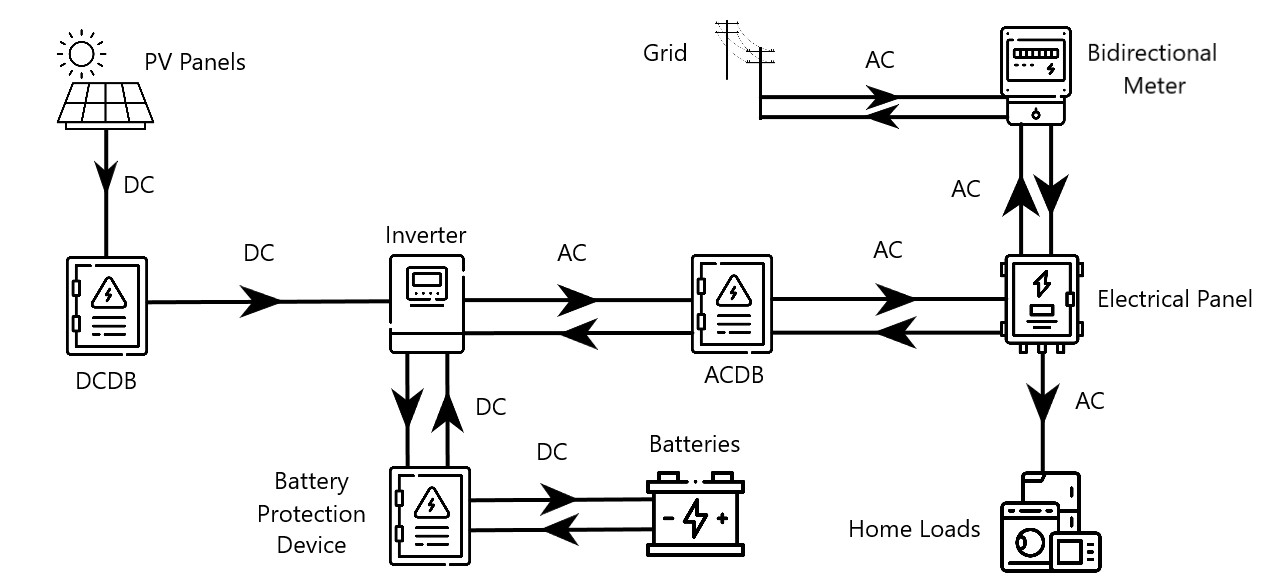
Components
- PV Panels: Photovoltaic panels absorb sunlight and convert it into Direct Current (DC).
- Inverter: Converts DC power into Alternating Current (AC) to power household loads, as all appliances run on AC.
- Batteries: Storage devices that store energy for use when solar generation or grid power is unavailable.
- DCDB (DC Distribution Board): Includes MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) and SPD (Surge Protection Device) to protect against current and voltage spikes on the DC side of the system.
- ACDB (AC Distribution Board): Includes MCB, SPD, and fuse to safeguard against voltage and current spikes on the AC side of the system.
- Battery Protection Device: Includes MCB or fuse to protect batteries from current and voltage spikes.
- Bidirectional Meter: Replaces the traditional unidirectional meter to accurately record both the import and export of energy to and from the grid.
- Electrical Panel: The existing panel in the customer's premises where solar power is connected to the household circuit for consumption and potential export.
- Lightning Arrestors: Protect PV panels and the system from damage caused by lightning strikes.
- Earthing: Safely dissipates surge currents resulting from lightning or within the system.
